Lecture 1 – Basic Concepts Introduction
evolution designed?
huh?
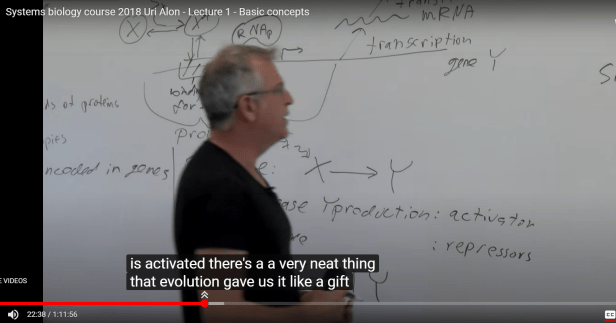
a very neat thing that evolution gave us like a gift?
huh?
cells think?
huh?
the promoter region of the gene can have several proteins (TF?) bound to it forming a landing pad for multiple combinations of different conditions X1 OR X2 AND X0 etc to allow the RNA Polymerase to work?
amazing programs?
huh?
Lecture 2 – Auto-regulation , a network motif
- complex networks are made of simple circuits – network motifs
- negative auto-regulation has useful functions: (a) speeds responses, (b) stabilizes against noise (robust)
Gene Regulation Networks
nodes X1, X2,…, Xn
arrows connecting the nodes Xi
Gene X encodes protein x which binds to promoter region for gene Y
X —> Y Activator (protein X increases production of protein Y)
X —| Y Repressor (protein X prevents production of protein Y)

dY/dt = B – A * Y
B: beta = protein production rate
A: alfa = protein removal by either breaking down or concentration dilution when the cell grows

Lecture 3 a – Feed Forward Loops
Lecture 3 b – Feed Forward Loop
Lecture 4 a – Temporal order, Global Structure, and Memory
Lecture 4 b – Temporal Order, Global Structure, and Memory
Lecture 5 a – Robustness using bifunctional components
Lecture 5 b – Robustness using bifunctional components
Lecture 6 a – Robustness in bacterial chemotaxis
Lecture 6 b – Robustness in bacterial chemotaxis
Lecture 7 a – Fold Change Detection
Lecture 7 b – Fold Change Detection
Lecture 8 a- Dynamic Compensation
Lecture 8 B – Dynamic Compensation
Lecture 8 C – Dynamic Compensation
Lecture 9 How to build a Biological Oscillator.
Lecture 10 Optimality in Biological Circuits